20CYS281-Operating-System-Lab
20CYS281 - Operating System Lab


MultiThreading
MultiThreading is a form of Multitasking where concurrent execution of the program happens. Process-based and thread-based concurrent executions or multitasking are supported. In process-based, it is concurrent execution of the programs whereas in thread-based concurrent execution of parts of the same program.
MultiThreading in C
C doesn’t support Multithreading. Only through POSIX Standards for threads (pthread) implementations are available.
Header file
#include <pthread.h>
Function
pthread_create(&thread_id, attr, myFunc, parameters);
- &thread_id - pointer to thread_id
- attr - thread attributes or NULL for default attributes
- myFunc - Function to be called once the thread is created
- parameters - parameters to the function (myFunc) called or NULL
pthread_join(thread_id, retval);
- thread_id - thread id
- retval - NULL
Example - Understanding pthread_create, pthread_join and pthread_exit
/*
@Author: Ramaguru Radhakrishnan
@Date: 30 - Dec - 2022
@Description: Creation and Execution of a simple thread using single parameter
*/
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void *summaclassdemo(void *args) {
printf("Welcome to the thread");
}
int main() {
pthread_t thread; // A thread ID is assigned
printf("%ld\n", thread);
// pthread_create(thread_id, thread_attribute/NULL,
// function,functon_params);
pthread_create(&thread, NULL, summaclassdemo, NULL);
pthread_join(thread, NULL);
//pthread_exit(NULL);
return 0;
}
Example Program 1 - Passing Single Parameter (Welcoming Different People - char array)
/*
@Author: Ramaguru Radhakrishnan
@Date: 21 - Dec - 2022
@Description: Creation and Execution of a simple thread using single parameter
*/
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// printWelcomeMessage will be called when the Thread is created in the main function
// which takes string as an argument
void *printWelcomeMessage(void *names) {
sleep(2);
char *name = (char *)names;
printf("\n[THREAD] Hello, Welcome %s.", name);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main () {
// thread defintion
pthread_t threads[7];
// parameter to be passed to the called function - printWelcomeMessage
char names[10][15] = {"Amritha","Praveen","Saurabh","Sangeetha","Lakshmy","Srinivasan","Ramaguru"};
int result;
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++ ) {
printf("\n[MAIN] Creating thread, %d", i);
// Creating the threading and thus calling the function with parameter passed to it
result = pthread_create(&threads[i], NULL, printWelcomeMessage, (void *)names[i]);
if (result) {
printf("Error in creating thread, %d ", result);
exit(-1);
}
}
// Exit the thread
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
Output
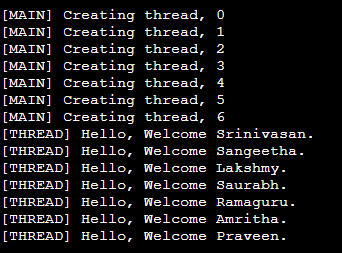
Example Program 2 - Passing Multiple Parameters (Addition of Two Numbers)
/*
@Author: Ramaguru Radhakrishnan
@Date: 21 - Dec - 2022
@Description: Creation and Execution of a simple thread using multiple parameters
*/
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// We should use structure to pass multiple arguments to a thread function
struct funcargs {
int a;
int b;
};
// addition will be called when the Thread is created in the main function
// which takes structure as an argument
void *addition(void *args) {
sleep(2);
struct funcargs *vars = (struct funcargs *)args;
printf("\n[THREAD] Hello, Addition of %d and %d is %d.", vars->a, vars->b, vars->a + vars->b);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main () {
// thread defintion
pthread_t threads;
// parameter to be passed to the called function - funcargs
struct funcargs vars;
vars.a = 10;
vars.b = 20;
int result;
printf("\n[MAIN] Creating thread");
// Creating the threading and thus calling the function with parameter passed to it
result = pthread_create(&threads, NULL, addition, (void *)&vars);
if (result) {
printf("Error in creating thread, %d ", result);
exit(-1);
}
// Exit the thread
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
Output
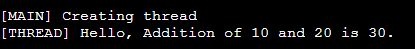
Example Program 3 - Passing Single Parameter and Joining the Threads (Welcoming Different People - char array)
/*
@Author: Ramaguru Radhakrishnan
@Date: 27 - Dec - 2022
@Description: Creation and Execution of a simple thread using single parameter and joining
*/
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// printWelcomeMessage will be called when the Thread is created in the main function
// which takes string as an argument
void *printWelcomeMessage(void *names) {
sleep(2);
char *name = (char *)names;
printf("\n[THREAD] Hello, Welcome %s.", name);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main () {
// thread defintion
pthread_t threads[7];
// parameter to be passed to the called function - printWelcomeMessage
char names[10][15] = {"Amritha","Praveen","Saurabh","Sangeetha","Lakshmy","Srinivasan","Ramaguru"};
int result;
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++ ) {
printf("\n[MAIN] Creating thread, %d", i);
// Creating the threading and thus calling the function with parameter passed to it
result = pthread_create(&threads[i], NULL, printWelcomeMessage, (void *)names[i]);
if (result) {
printf("Error in creating thread, %d ", result);
exit(-1);
}
}
pthread_join(threads[0], NULL);
pthread_join(threads[1], NULL);
pthread_join(threads[2], NULL);
pthread_join(threads[3], NULL);
pthread_join(threads[4], NULL);
pthread_join(threads[5], NULL);
pthread_join(threads[6], NULL);
// Exit the thread
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
Example Program 4 - Passing Multiple Parameter and Joining the Threads (Student Marks Calculation)
/*
@Author: Ramaguru Radhakrishnan
@Date: 31 - Dec - 2022
@Description: Creation and Execution of a simple thread using multiple parameters
*/
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
// We should use structure to pass multiple arguments to a thread function
struct funcargs {
int rollnumber;
char name[10];
int mark1;
int mark2;
int mark3;
int mark4;
int mark5;
};
// addition will be called when the Thread is created in the main function
// which takes structure as an argument
void *calculateTotal(void *args) {
struct funcargs *vars = args;
printf("\n[THREAD] Hello, The total for %s with Roll Number %d is %d.", vars->name, vars->rollnumber, vars->mark1 + vars->mark2 + vars-> mark3 + vars-> mark4 + vars->mark5);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main () {
// thread defintion
pthread_t threads;
// parameter to be passed to the called function - funcargs
struct funcargs vars;
//printf("\n[Main] %p", vars);
//printf("\n%p", &vars);
vars.rollnumber = 18;
strcpy(vars.name,"Ramaguru R");
vars.mark1 = 99;
vars.mark2 = 87;
vars.mark3 = 47;
vars.mark4 = 78;
vars.mark5 = 66;
int result;
printf("\n[MAIN] Creating thread");
// Creating the threading and thus calling the function with parameter passed to it
result = pthread_create(&threads, NULL, &calculateTotal, (void *)&vars);
if (result) {
printf("Error in creating thread, %d ", result);
exit(-1);
}
// Exit the thread
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
Example Program 5 - Passing Single Parameter and Factorial Example (int value)
/*
@Author: Ramaguru Radhakrishnan
@Date: 03 - Jan - 2023
@Description: Creation and Execution of a simple thread using single parameter
*/
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void *fact(void *args) {
int n = (int )args;
int fact = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
fact = fact * i;
}
printf("\nThe factorial is %d", fact);
}
int main() {
pthread_t thread[5]; // A thread ID is assigned
int n = 5;
int c = 10;
int k = 4 ;
int p = 8;
// pthread_create(thread_id, thread_attribute/NULL,
// function,functon_params);
pthread_create(&thread[0], NULL, fact, (void *) n);
pthread_create(&thread[1], NULL, fact, (void *) k);
pthread_create(&thread[2], NULL, fact, (void *) p);
pthread_create(&thread[3], NULL, fact, (void *) c);
pthread_join(thread[0], NULL);
pthread_join(thread[1], NULL);
pthread_join(thread[2], NULL);
pthread_join(thread[3], NULL);
return 0;
}
