20CYS281-Operating-System-Lab
20CYS281 - Operating System Lab


Mutex
Mutex is Mutual Exclusion Object. At any point of time, only one thread can work with the shared resources. In simple words, it is a locking mechanism.. A thread acquires a mutex when it is entering to access the shared/critical section of the program. The thread releases the mutex when it is exiting the shared/critical section of the program. A mutex can either be locked or unlocked which is modified only the process which requested or released the lock.
Function
pthread_mutex_init(&lock, *attr);
- &lock - mutex (defined using pthread_mutex_t)
- attr - mutex attributes or NULL for default attributes
pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
- &lock - mutex (that was initialized using pthread_mutex_init)
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
pthread_mutex_trylock(&lock);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
- &lock - mutex (that was initialized using pthread_mutex_init)
Example 1 - Mutex
/*
@Author: Ramaguru Radhakrishnan
@Date: 28 - Dec - 2022
@Description: Mutex
*/
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// Mutex lock
pthread_mutex_t lock;
// Counter is the shared resource variable accessed by all threads
int counter;
// printWelcomeMessage will be called when the Thread is created in the main function
// which takes string as an argument
void *printWelcomeMessage(void *names) {
// Thread acquiring the lock
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
char *name = (char *)names;
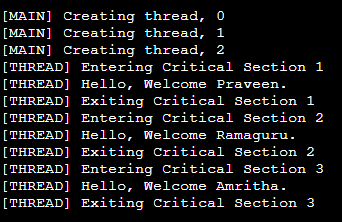
printf("\n[THREAD] Entering Critical Section %d", ++counter);
for(int i=0; i<400000000;i++);
printf("\n[THREAD] Hello, Welcome %s.", name);
printf("\n[THREAD] Exiting Critical Section %d", counter);
// Thread releasing the lock
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
int main () {
// thread defintion
pthread_t threads[3];
// parameter to be passed to the called function - printWelcomeMessage
char names[10][15] = {"Amritha","Praveen","Ramaguru"};
// initializing the mutex
if (pthread_mutex_init(&lock, NULL) != 0)
{
printf("\n mutex init failed\n");
return 1;
}
int result;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++ ) {
printf("\n[MAIN] Creating thread, %d", i);
// Creating the threading and thus calling the function with parameter passed to it
result = pthread_create(&threads[i], NULL, printWelcomeMessage, (void *)names[i]);
if (result) {
printf("Error in creating thread, %d ", result);
exit(-1);
}
}
pthread_join(threads[0], NULL);
pthread_join(threads[1], NULL);
pthread_join(threads[2], NULL);
// destroying the mutex
pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
}
Output